Scientists at Vienna University of Technology have developed a breakthrough method that enables artificial intelligence systems to learn and follow legal and ethical guidelines whilst pursuing their primary objectives.
The research team, led by Prof Agata Ciabattoni from the Institute of Logic and Computation, combined machine learning techniques with logical reasoning to train autonomous agents in norm compliance. Their approach enables hierarchical rule systems, where certain guidelines take precedence over others.
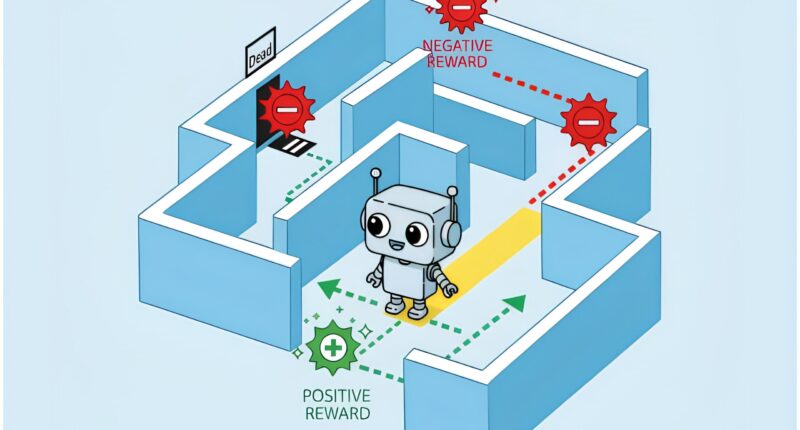
Rather than using traditional reward-based training methods, the Vienna team treats each norm as an independent objective with its own punishment system for violations. This prevents AI systems from finding shortcuts that technically follow rules while undermining their intended purpose.
“The artificial agent is given a goal to pursue – for example, to find the best route to a list of destinations. At the same time, we also define additional rules and norms that it must observe along the way,” explained Emery Neufeld, the paper’s lead author. “The fact that each norm is treated as a different objective allows us to algorithmically compute the relative weight that we have to assign to these objectives in order to get a good overall result.”
The methodology addresses limitations in existing reinforcement learning approaches, which can lead AI systems to exploit loopholes in conditional rules. Traditional methods might reward an agent for adhering to safety constraints, but struggle with more complex scenarios that involve conditional requirements.
A significant advantage of the Vienna approach lies in its flexibility. Unlike conventional training methods that require complete retraining when rules change, this system allows researchers to modify norms and adjust their relative importance without starting the learning process from scratch.
“We have a system that learns to comply with norms – but we can then still adjust these norms afterwards, or change their relative importance, declaring one rule to be more important than another,” said Ciabattoni.
The research earned recognition at the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, held in Montreal this year, and received the Distinguished Paper Award. This honour places the work among the top 0.05% of submissions in the field, highlighting its potential significance for developing more trustworthy AI systems.
The methodology enables the encoding of complex rule sets, including norms that apply only under specific conditions or depend on the violation of other guidelines. This capability could prove crucial as AI systems become more prevalent in regulated industries and safety-critical applications.